When the Crystal Palace and Park opened in south London in 1854, it was an instant sensation. Visitors came from far and wide to see the giant glass structure that had been rebuilt there, bigger and better, after the Great Exhibition of 1851 in Hyde Park. Wide-eyed spectators wandered freely through Egyptian and Medieval Courts, delighted in high-wire circus acts, and were transported by a 4,000-piece orchestra.
Tucked away in a corner of the vast gardens that fanned out from the palace, past sweeping terraces and more fountains than even at Versailles, was a smaller but no less ambitious attraction. Scattered across several islands in the middle of a lake stood three dozen life-size sculptures of prehistoric animals, including several dinosaurs up to 30 feet long—the world’s first attempt to model them at full scale.
The Crystal Palace Dinosaurs were the work of Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins, a natural history artist who, aided by some of the leading scientists of the day, had dreamt up a grand experiment in visual education, bringing to life the “dry bones or oddly shaped stones” found in the British Museum and introducing the masses to the burgeoning science of paleontology. By reconstructing Britain’s long-extinct animals, he hoped to “render the appearance and names of the ancient inhabitants of our globe as familiar as household words.”
A print showing the dinosaur sculptures within the wider park surrounding the newly erected Crystal Palace in Sydenham, likely from 1854.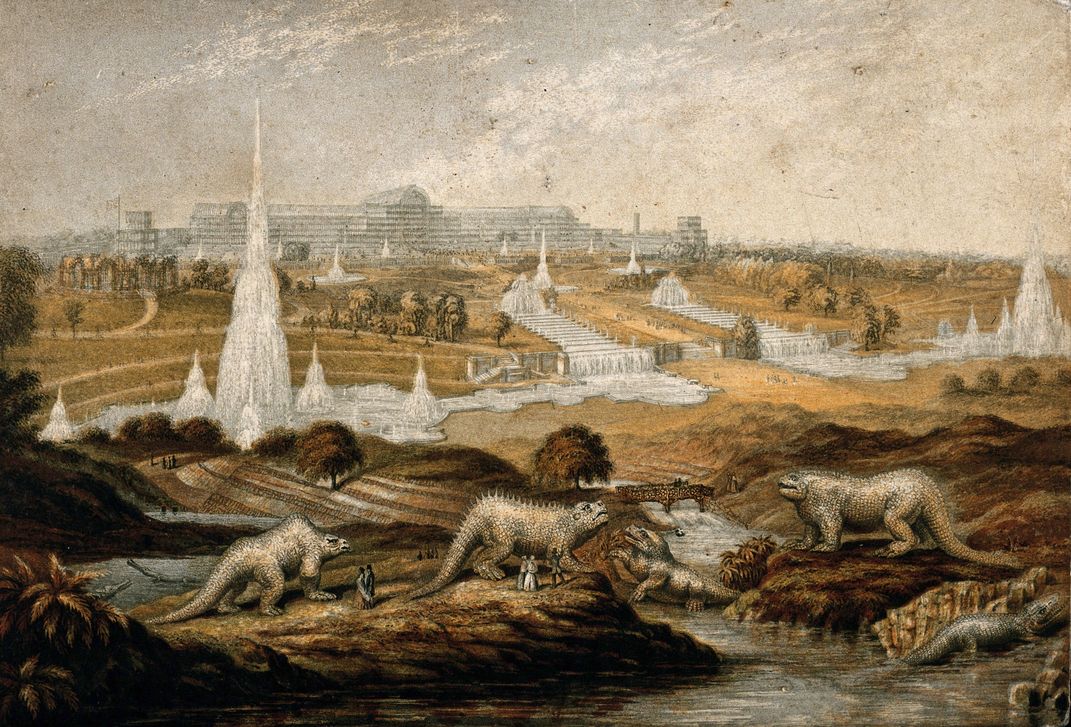
The palace burned down in the 1930s, but, almost 170 years after they were crafted, most of Hawkins’ original sculptures still stand sentry in the park. Today, they’re mostly famous for being wildly inaccurate. With few complete fossils to work off, Hawkins had to use his imagination and the advice of comparative anatomists to breathe life into his models, which, in addition to four true dinosaurs, also depict prehistoric mammals, reptiles and amphibians. As a result, the sculptures look suspiciously like many modern-day creatures.
“People kind of scoff and giggle, because they look so wrong today, but at the time they…
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at Travel | smithsonianmag.com…
